All functions curleasygetinfo curleasyinit curleasyperform curleasyreset curleasysetopt curlmultiaddhandle curlmultiinit curlmultiperform curlmultiremovehandle curlmultisetopt curl / libcurl / API / Examples / http-post.c. Bitwarden safari. To get curl to show detailed information about a single file, you should use -I / -head option. It displays all available info on a single file for HTTP and FTP. The HTTP information is a lot more extensive. For HTTP, you can get the header information (the same as -I would show) shown before the data by using -i /.
cURL is the magical utility that allows developers to download a URL's content, explore response headers, get stock quotes, confirm our GZip encoding is working, and much more. One more great usage of cUrl for command line is POSTing form data to a server, especially while testing moderate to advanced form processing. And just like other cURL commands, POSTing form data is incredibly simple.
POSTing Form Data with cURL
Start your cURL command with curl -X POST and then add -F for every field=value you want to add to the POST:
If you were using PHP, you could use print_r on the $_POST variable to see that your server received the POST data as expected:
If you need to send a specific data type or header with cURL, use -H to add a header:
POSTing Files with cURL
POSTing a file with cURL is slightly different in that you need to add an @ before the file location, after the field name:
Using PHP to explore the $_FILES variable array would show file data as though it was uploaded via a form in browser:
POSTing file contents with cURL is Probably easier than you thought, right?
The first time I needed to POST file data from command line I thought I was in for a fight; instead I found that cURL made the process easy!
cURL is a free and open-source command-line utility used for transferring data to or from a remote host with minimal user interaction. cURL works with primary protocols like HTTP, FTP, SCP, and SFTP.
It allows users to upload and download data either using single commands or bash scripts. It also provides features such as user-authentication, proxy tunneling, download resume, form-based uploads, SSL certificates, and so much more. It is safe to say that cURL is more than an HTTP client.
This tutorial will walk you through one cURL functionality that allows users to perform HTTP post requests using file data.
Before we get started, let me mention that this is not a beginner’s guide to cURL; you need a degree of prior know-how, especially knowledge of network protocols, HTTP requests, and more.
Before we can dive into using cURL to carry out POST requests, let us first get setup.
How to Install cURL
In most cases, you will find cURL installed in major Linux distributions by default. To confirm you have cURL, use the command
If you get an error:
You will need to install it before proceeding.
Use the default package manager to complete the installation as shown in the commands below:
Before discussing how to POST data from a file with cURL, allow me to talk about the POST request in brief. As usual, if you are already familiar with this, you can feel free to skip ahead; otherwise, stick around.
cURL POST Request
Curl Post Example
The HTTP post request is one of the most popular HTTP/HTTPS request methods used to send data to a remote host to create or update a resource.
Now:
Curl Post With Body
Please do not confuse the method with PUT; although they’re quite similar, they have their differences.
Curl Post Data Json
The data sent using a POST request is mainly stored in the request body of the HTTP request.
For example, consider the below POST request that sends username and password as well as their values.
To send the above POST request using cURL, we can specify the commands as: Tipsy bartender margarita fruit salad.
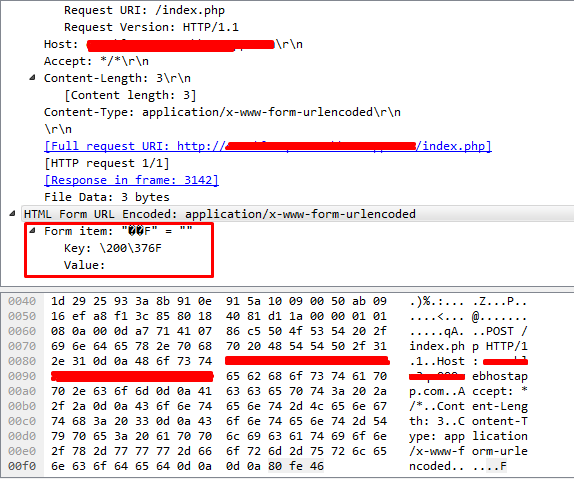
In the above command, we used the -d option to tell cURL to include the default headers, which is Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
The -X option specifies the HTTP request method to use, in this case, HTTP POST request.
cURL Specify Content-Type
In some cases, we might want to specify [explicitly] the Content-Type when sending the request. The Content-Type entity in the header specifies the type of media of the resource we are sending. The media type is also commonly known as the MIME Type.
If you wish to learn about MIME Types, consider the resource provided below:
To specify the Content-Type in a cURL request, we can use the -H flag. For example, let us send MIME Type of application/JSON.
The above specifies that we want to send a JSON object to the provided URL. You can use this to read the values from a JSON file or send it as raw.
How to Read Data from a File
Suppose you want to make requests in the command-line using cURL, but you have the data to send stored in a file. You can use the Content-Type to specify the media type and then pass the file path containing the data. For this example, I will illustrate using a JSON object.
The JSON file (data.json) contains the following values:
To send this data from a JSON file, we can use the -d and then pass the filename as shown in the command below:
You can also use the –data-binary option.
Curl Post Data Example
You can also use a text file to send the data; all you need to specify is the Content-Type as text/plain.

For example, a text file (data.txt) containing the following values
Using the cURL command, simply send the request as:

You can use other file types you can use such as XML, HTML, and many more.
Conclusion

In this tutorial, we have discussed how to make POST requests and pass data in various formats. It is good to keep in mind that besides being very powerful, cURL is also very flexible. It can combine a collection of options in a single command to create powerful requests. For more information, I recommend the cURL documentation as it is well written.
Curl Post Data-binary
Thank you for reading, and have fun with cURL.

_Cisco_Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client_vpncli.exe.png)